There are several ways to show progress of a running background tasks in Visual Studio. Here’s how to use them from your own extensions.
Status bar
The status bar has its own progress indicator and it is the easiest place to show progress to the user. It’s visible, but doesn’t demand attention from the user and isn’t blocking them in doing what they are currently doing. This is a good option for most background tasks.

Using the API to show the status bar progress is fairly simple:
await Task.Delay(1000); // long running task
await VS.StatusBar.ShowProgressAsync("Step 1/3", 1, 3);
await Task.Delay(1000); // long running task
await VS.StatusBar.ShowProgressAsync("Step 2/3", 2, 3);
await Task.Delay(1000); // long running task
await VS.StatusBar.ShowProgressAsync("Step 3/3", 3, 3);
// Progress ends as current step (3) and total steps (3) are equal
Threaded Wait Dialog
The Threaded Wait Dialog (TWD) is a progress indicator dialog that only pops up if the background task takes longer than x number of seconds specified by the extender. It writes progress to the status bar the whole time, but will show the dialog after x number of seconds running.
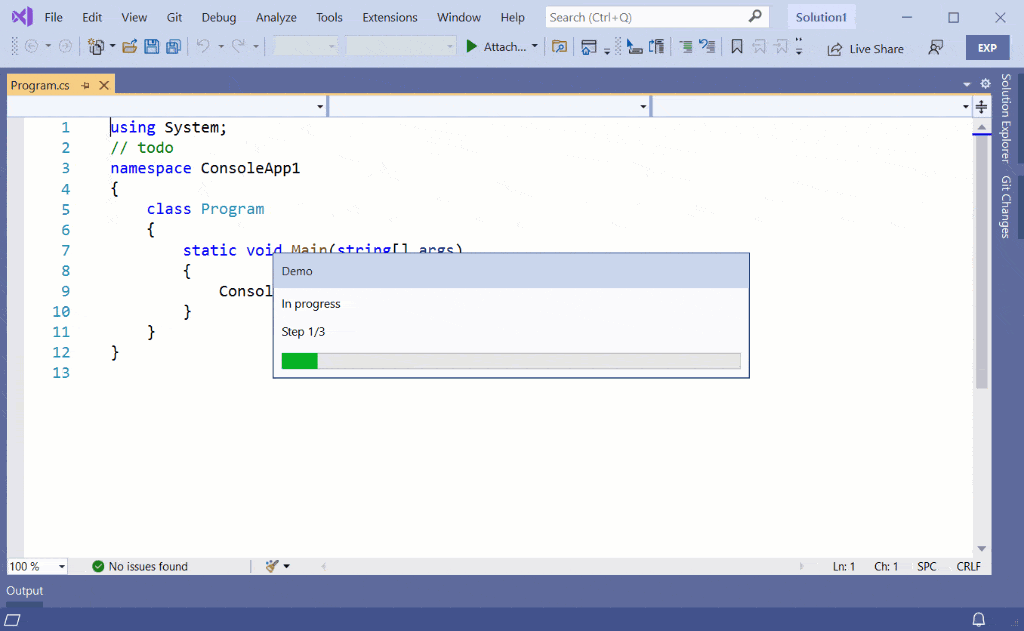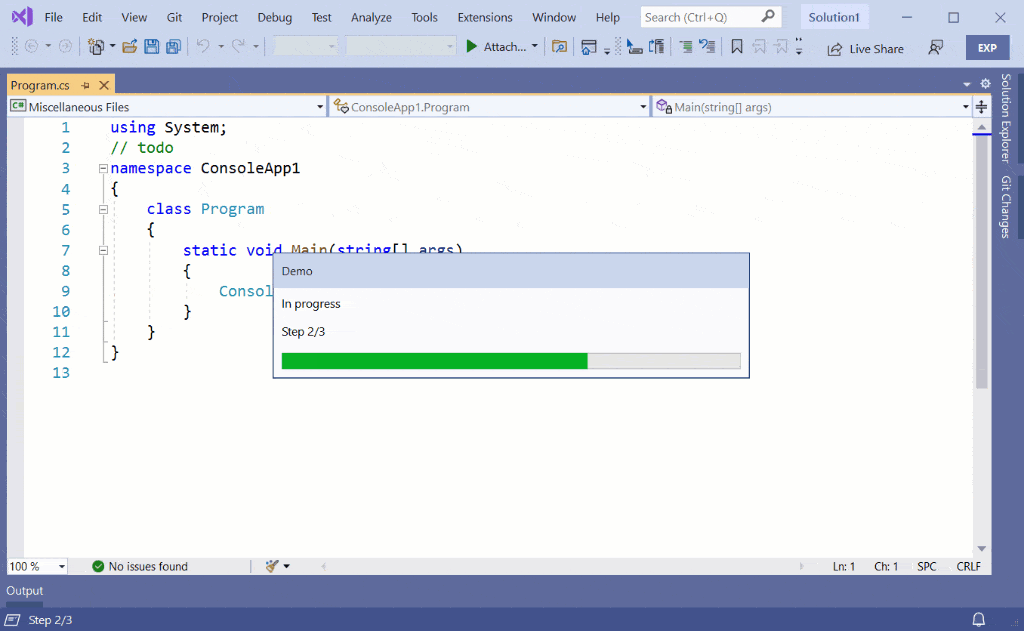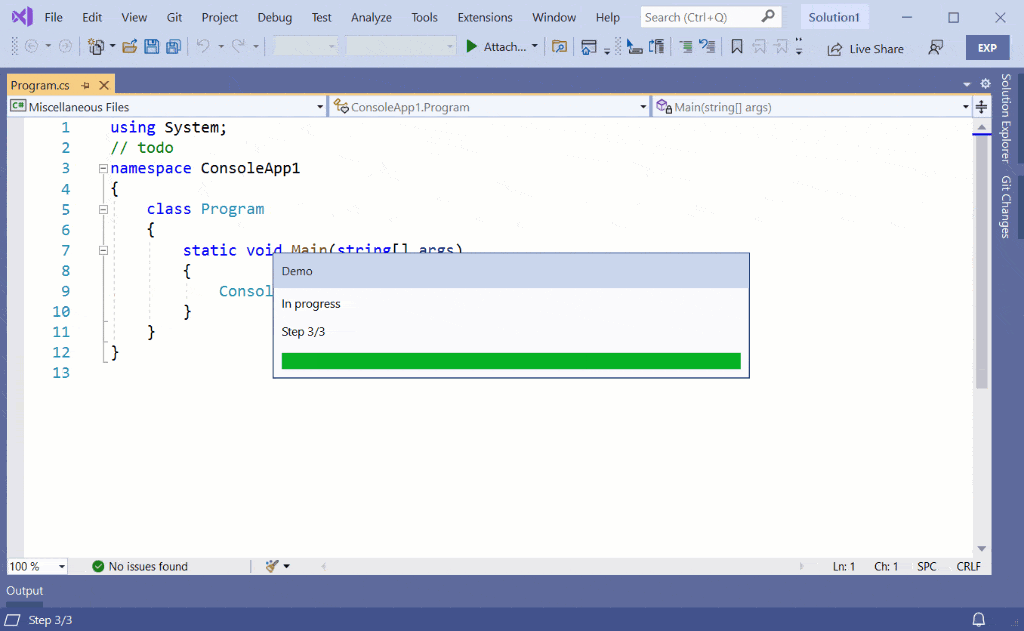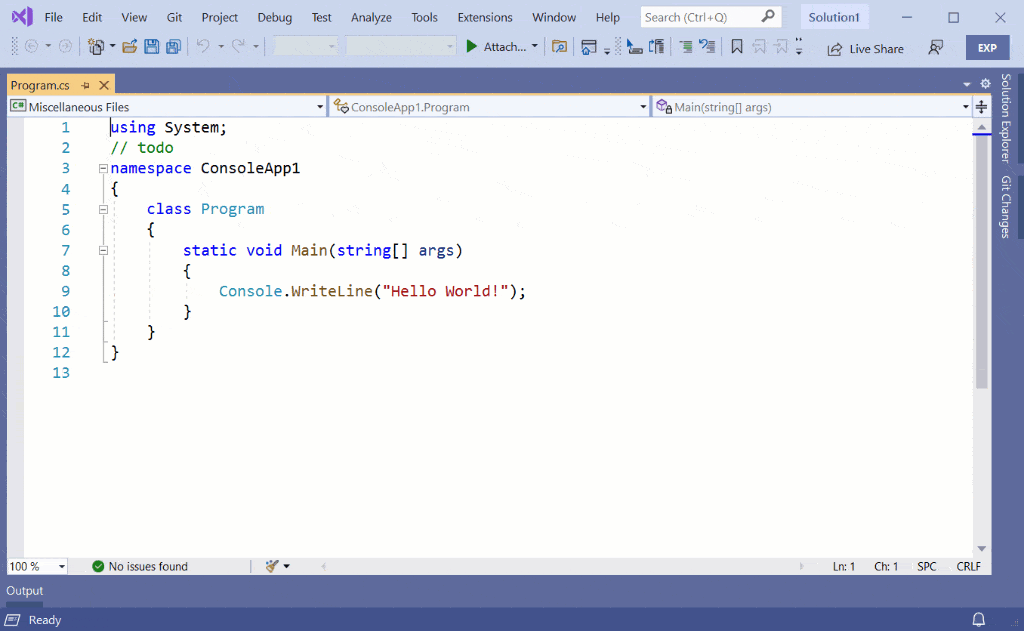
The TWD cannot be shown whenever you want to. It is managed by Visual Studio such that it doesn’t interfere the end user too often. Using it requires more code than just using the Status Bar, but it is still a relatively simple API to use:
var fac = (IVsThreadedWaitDialogFactory)await VS.Services.GetThreadedWaitDialogAsync();
IVsThreadedWaitDialog4 twd = fac.CreateInstance();
twd.StartWaitDialog("Demo", "Working on it...", "", null, "", 1, true, true);
var totalSteps = 3;
for (var currentStep = 1; currentStep <= totalSteps; currentStep++)
{
var text = $"Step {currentStep}/{totalSteps}";
twd.UpdateProgress("In progress", text, text, currentStep, totalSteps, true, out _);
await Task.Delay(1000); // long running task
}
twd.EndWaitDialog();
(twd as IDisposable).Dispose();
Task Status Center
At the bottom left corner of the status bar is the Task Status Center (TSC). It is used to report progress on long running background tasks and is used by many services in Visual Studio.
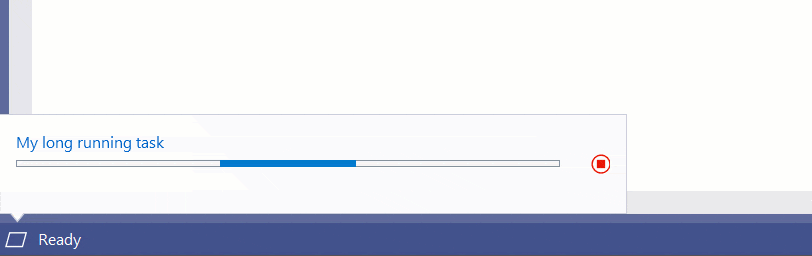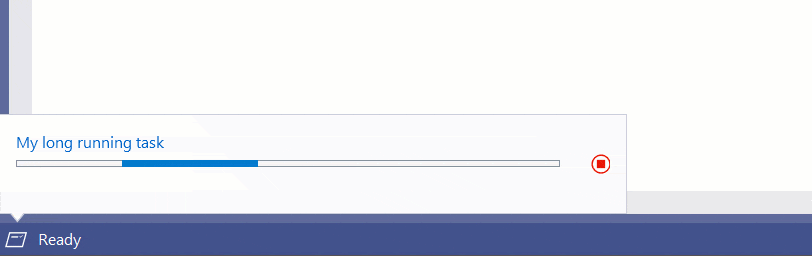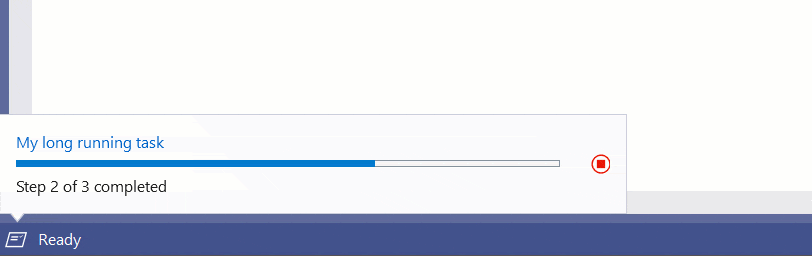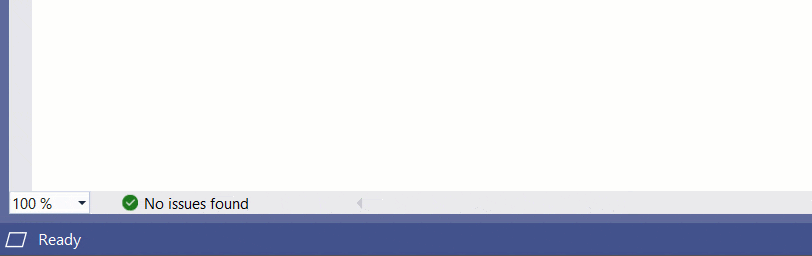
The API has more concepts than using the other methods of showing progress.
private async Task StartAsync()
{
IVsTaskStatusCenterService tsc = await VS.Services.GetTaskStatusCenterAsync();
var options = default(TaskHandlerOptions);
options.Title = "My long running task";
options.ActionsAfterCompletion = CompletionActions.None;
TaskProgressData data = default;
data.CanBeCanceled = true;
ITaskHandler handler = tsc.PreRegister(options, data);
Task task = LongRunningTaskAsync(data, handler);
handler.RegisterTask(task);
}
private async Task LongRunningTaskAsync(TaskProgressData data, ITaskHandler handler)
{
float totalSteps = 3;
for (float currentStep = 1; currentStep <= totalSteps; currentStep++)
{
await Task.Delay(1000);
data.PercentComplete = (int)(currentStep / totalSteps * 100);
data.ProgressText = $"Step {currentStep} of {totalSteps} completed";
handler.Progress.Report(data);
}
}